What is Linear Data Structure?
A linear data structure is one in which data items are ordered sequentially or linearly, with each member attached to its previous and next neighboring elements. All the elements in the linear data structure can be traversed in a single run. Arrays, Linked List, Stack and Queue are the different types of linear data structures available.
Takeaways
The time complexity of linear data structure increases with the increase in the input size.
Introduction to Linear Data Structure
A linear data structure is one in which data items are ordered sequentially or linearly, with each member attached to its previous and next neighboring elements.
Since the data elements are stored in a linear fashion, the structure allows single-level data storage. As a result, traversal of the data is accomplished in a single run. Memory is not efficiently utilized in a linear data structure.
Characteristics of Linear Data Structure
The linear data structure has the following characteristics:
- It's a data structure that stores and manages data in a linear order .
- The sequence's data elements are linked to one another in sequential order .
- Since data is organized sequentially, implementing the linear structure in a computer's memory is simple.
- Since the data elements are stored in a single level, traversing them in a single run is possible.
- If a structure for storing data linearly is implemented, the computer's memory will be underutilized.
- The time complexity of a data structure increases with increase in the size of the data structure.
List of data structure in a linear type of data structure
different types of the linear data structures are:
Array
The array is the linear data structure that is a collection of similar data items stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements of the array are stored in one memory block for the entire array.
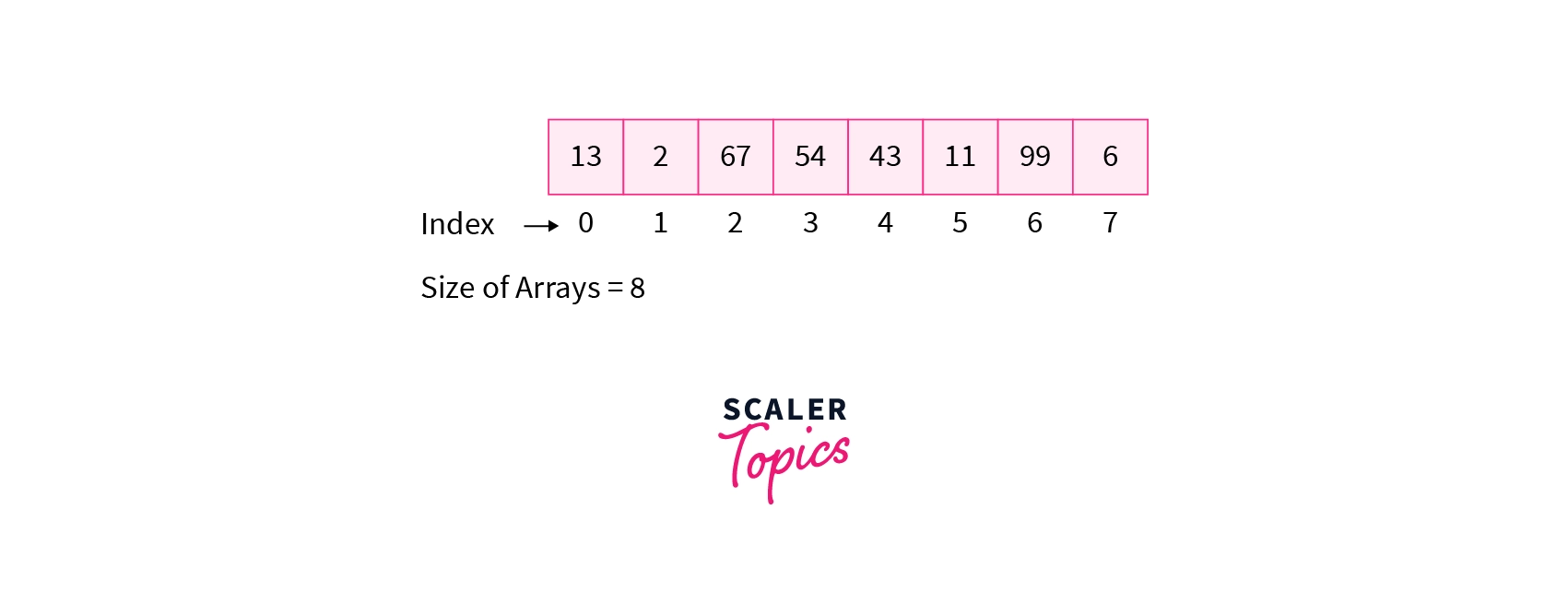
Now let's understand the properties of array that are as follows:
- In an array , elements are stored in a contiguous manner.
- The elements inside the array can be accessed in constant time.
- The time complexity of searching an element inside an array will be proportional to the size of the array in the worst case i.e. O (size of the array).
- The element can be inserted at the end of a dynamic array in O(1) time. But to insert the element in the beginning or in the middle we need to shift the element towards the right to create a space. So, the time complexity will be proportional to the size of the array i.e. O (size of the array).
- The element can be deleted from the end in O(1) time. But to delete the element from the beginning or from the middle the time complexity will be proportional to the size of the array i.e. O (size of the array).
Linked List
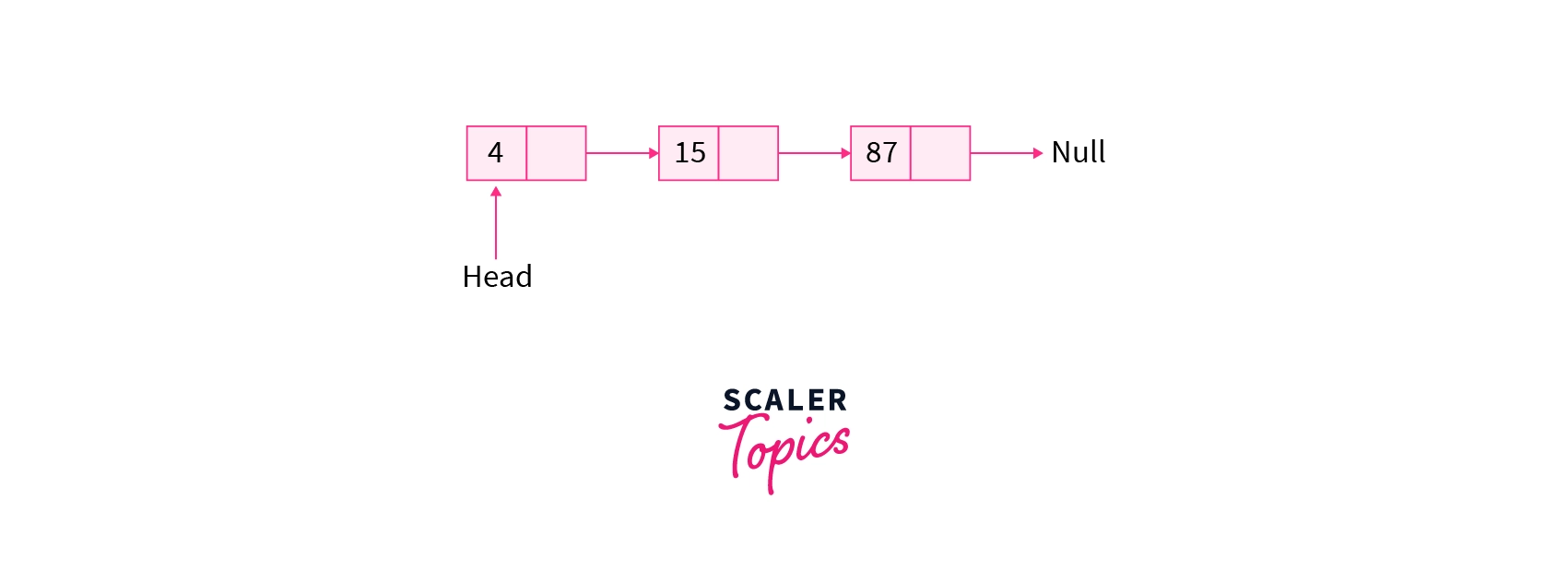
A linked list is the linear data structure made up of nodes, each of which has a data field and a connection to the next node in the list. The first node is pointed to by the head pointer, and the last element points to NULL marking the end of the linked list as shown in below figure.
NOTE: The head pointer points to null when the list is empty
These are the following types of Linked List:
- Singly Linked List: It consists of a series of a structure called nodes and each node contain data part and pointer to the next node in the linked list therefore it allows traversal in a single direction.

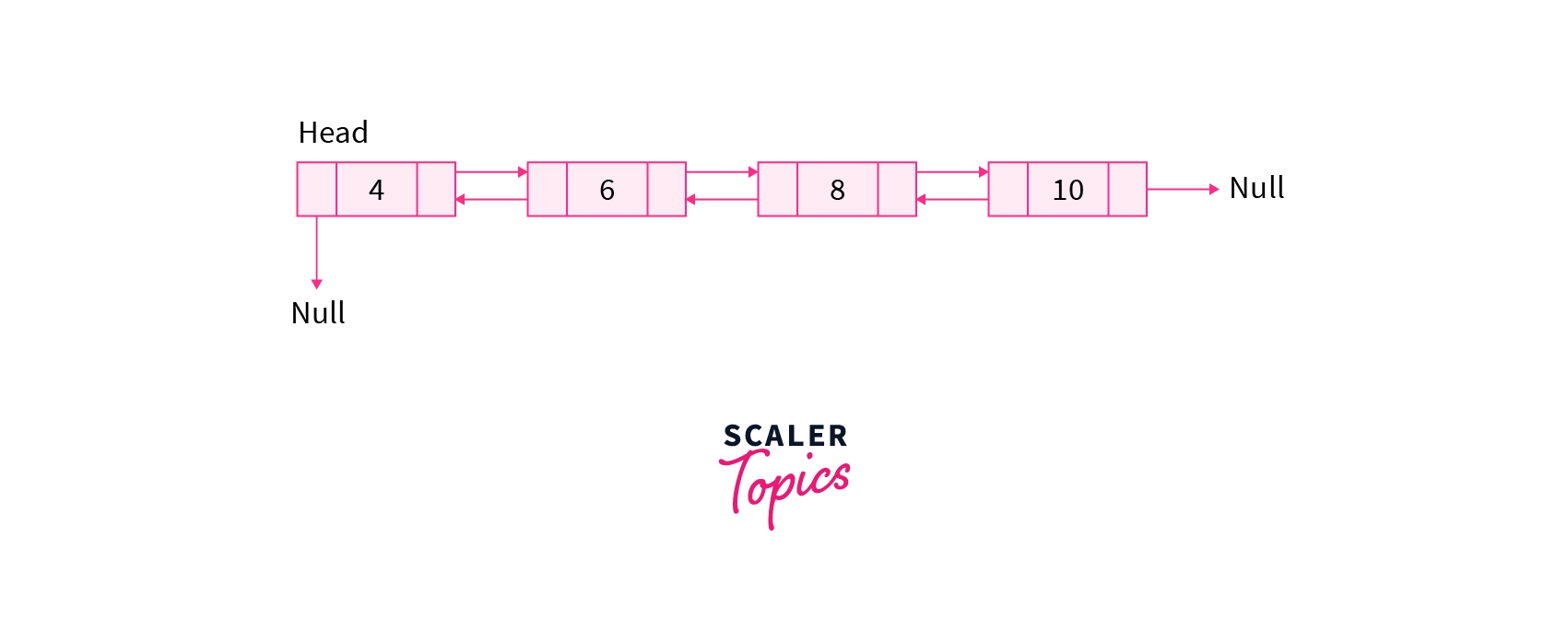
- Doubly Linked List: In this type of linked list , a node contains a pointer to the previous as well as the next node in the sequence i.e. in a doubly-linked list , a node consists of three parts: data, a pointer to the next node in the sequence, and a pointer to the previous node. The advantage of this type of linked list is that we can traverse in both directions.
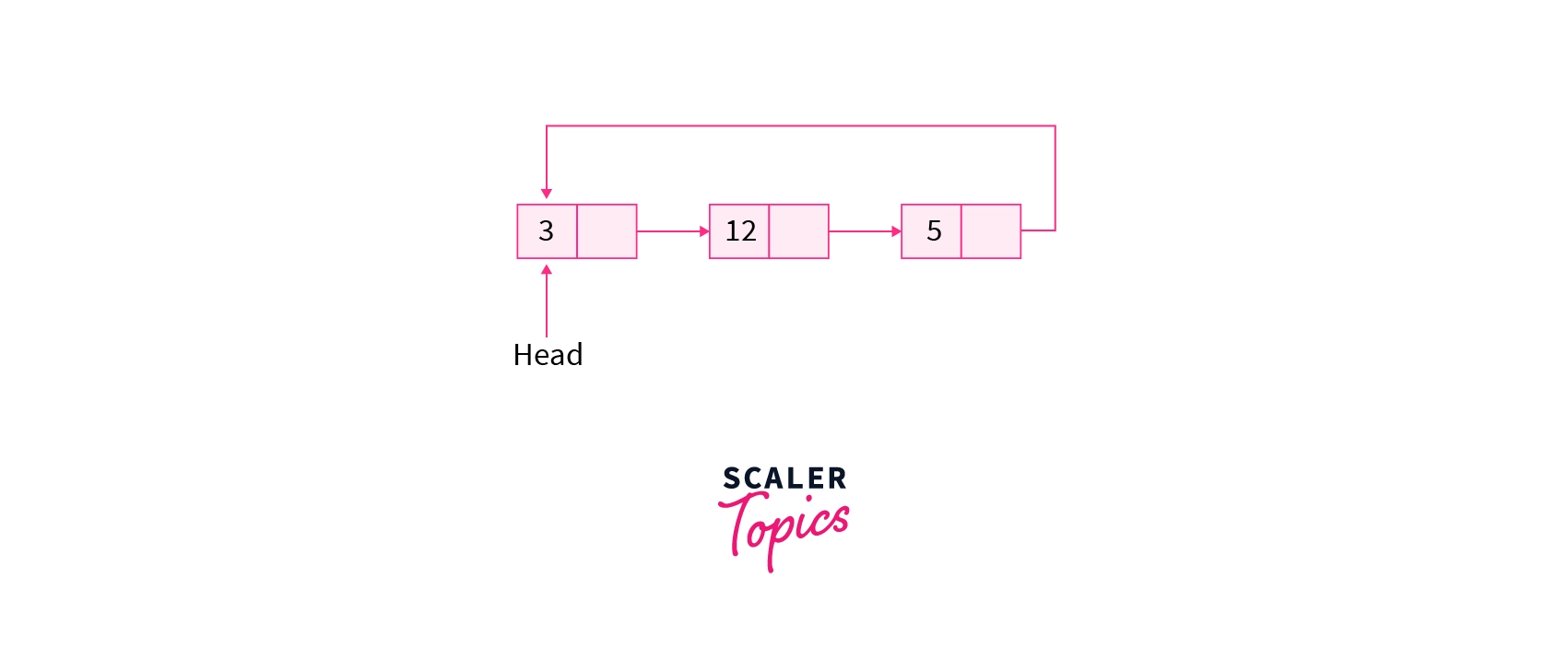
- Circular Linked List: Each node in a singly-circularly-linked list contains one link, just like in a regular singly-linked list, except the last node's next link points back to the first node. Thus circular linked list do not have ends i.e. every node points to its next node in the sequence but the last node points to the first node in the list.
Properties of Linked List:
Now let's understand the important properties of linked list :
- To access the particular element in the linked list we have to traverse nodes starting from the first one to the last one. So in the worst-case time complexity of accessing an element in the linked list is O(n) , where ' n ' can be assumed as the size of the linked list.
- To search for the element in the linked list we have to traverse all the nodes in the worst case. So the time complexity of searching an element inside linked list is O(n) .
- We can insert an element in the linked list at the start or at the end or at any given position but the time complexity will varies accordingly. Inserting a node, in the beginning, will take O(1) time because we need to modify only two pointers. But inserting a node at any particular position will take O(n) time because in the worst case we may need to insert a node at the end of the linked list.
- The time complexity of the delete operation in the linked list will be O(n) for scanning the list of size n to search for the particular element to be deleted.
Stack
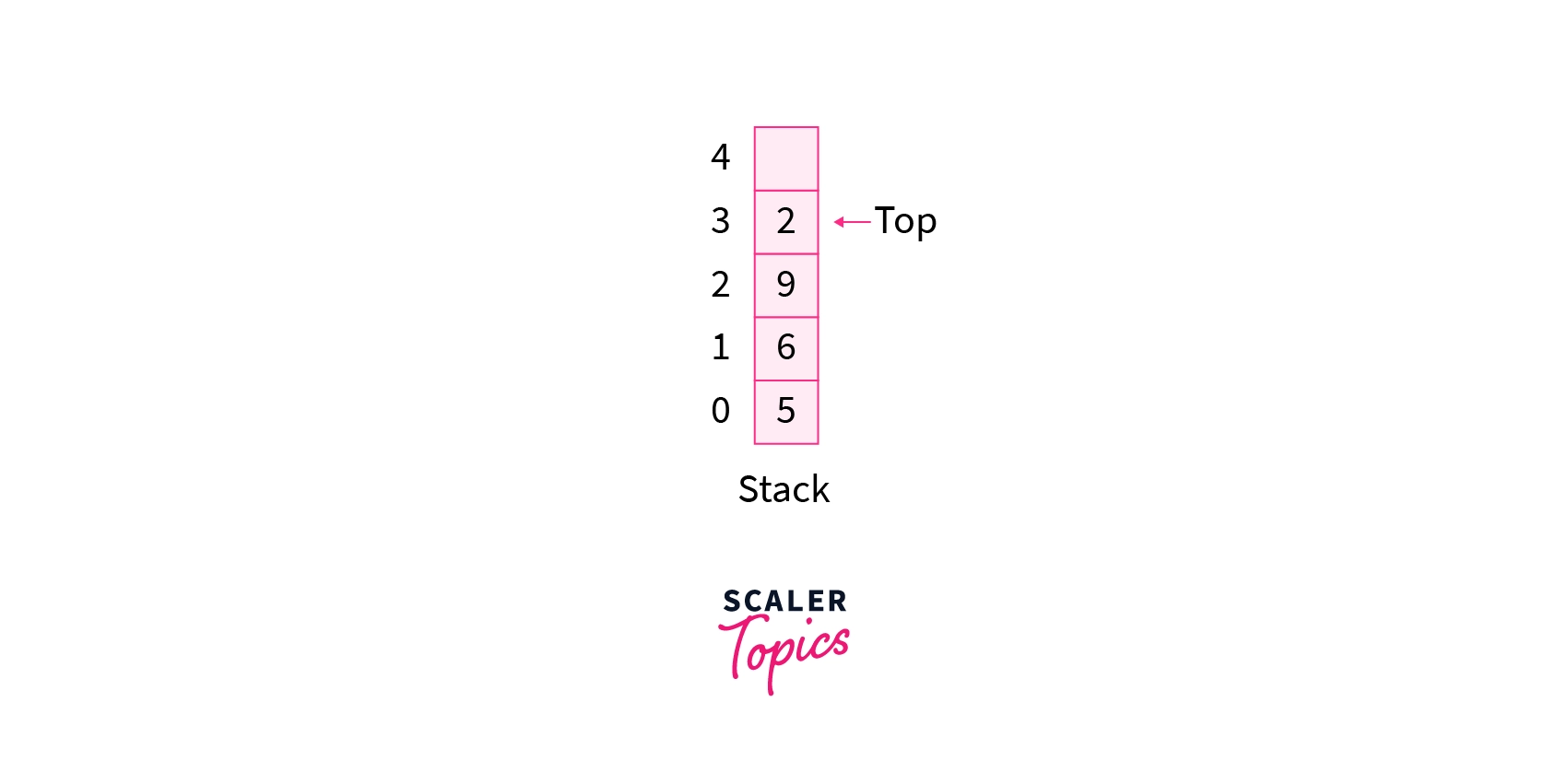
A stack is a simple data structure used for storing data. A pile of plates in a cafeteria is a good example of a stack. The piles are added to the stack as they are cleared and they are placed on the top. When a plate is needed, it is taken from the stack's top. The first plate on the stack is the last one to be used.
 stack data structure" width="864" height="200" />
stack data structure" width="864" height="200" />
A stack is an ordered list in which insertion and deletion are performed at one end, which is referred to as the top. The first element to be eliminated is the last one that was entered. As a result, it's known as the Last in First Out (LIFO) . When an element is inserted in a stack, the concept is called push and when the element is removed from the stack, the concept is called pop. Trying to pop out an empty stack is called underflow and trying to push an element in a full stack is called overflow.
There are the following operations that can be performed on the stack(For simplicity, assume the data is an integer type):
- void push(int data): Data can be inserted from the top of the stack. The time complexity of this operation is O(1) .
- int pop(): This operation is used to remove the last inserted element from the top of the stack. The time complexity of this operation is O(1) .
- int top(): This operation is used to return the last element without removing it. The time complexity of this operation is O(1) .
- int size(): This operation is used to return the number of elements stored in the stack. The time complexity of this operation is O(1) .
- int isEmpty(): It is used to indicate whether any elements are stored in the stack or not. The time complexity of this operation is O(1) .
Queue
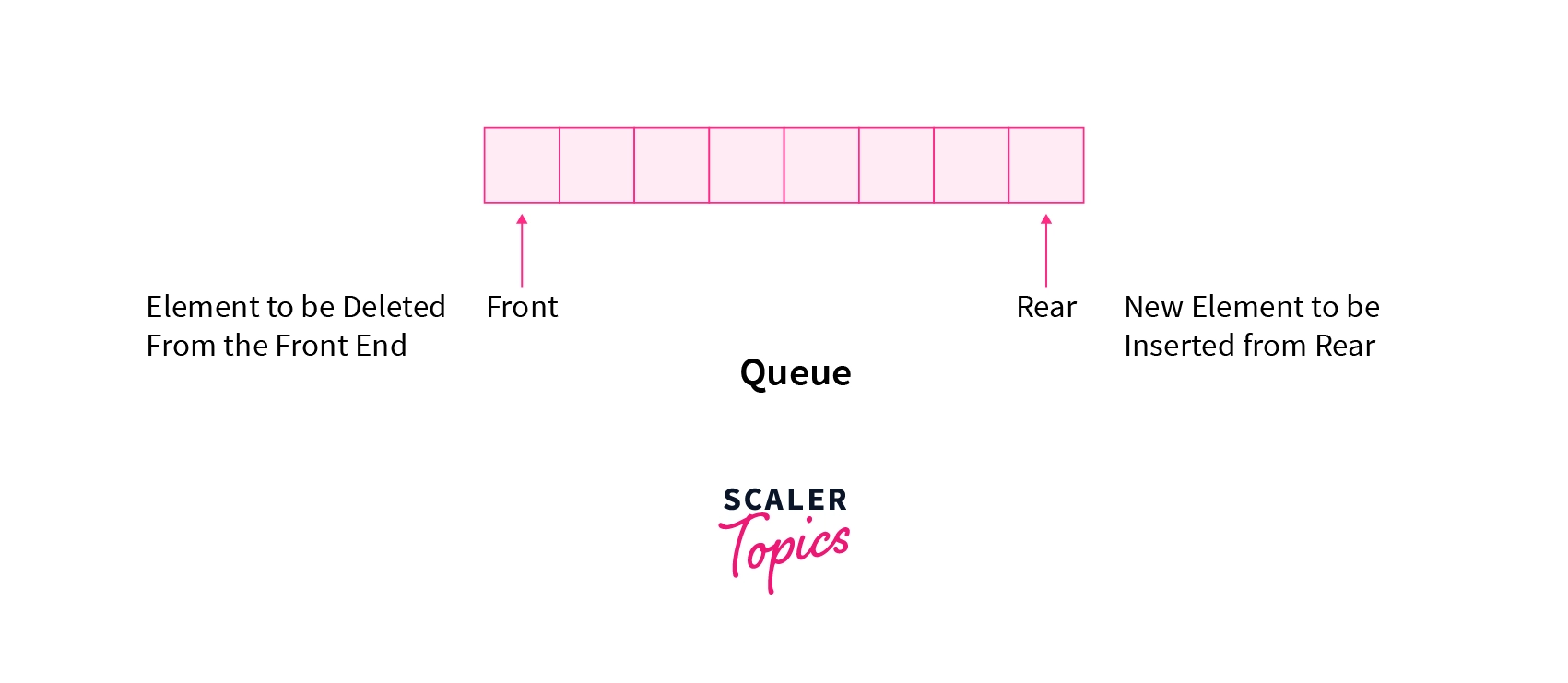
A queue is another linear data structure that is used for storing data. In the queue, the order in which data arrives is important. In general, a queue is a line of people or things to be served in sequential order starting at the beginning of the line or sequence. A queue is an ordered list in which insertions are done at one end i.e. rear end and deletions are done at the other end i.e. front end. The first element to be added is also the first to be removed. As a result, it's known as "First in, First out" (FIFO) .
The two changes that can be made to a queue are given special names, similar to Stacks. The concept of EnQueue is used when an element is added to a queue, and DeQueue is used when an element is deleted from the queue. Underflow refers to dequeuing an element from an empty queue, while overflow refers to enqueuing an element from a filled queue.
There are the following operations that can be performed on the queue(For simplicity, assume the data is an integer type):
- void enQueue(int data): This operation is used for inserting an element in the queue at the rear end. The time complexity for this operation is O(1) .
- int deQueue(): It is used to remove and return the element from the front of the queue. It will take O(1) time.
- int front(): It returns the element at the front without removing it. The time complexity for this operation is O(1) .
- int rear(): It returns the element at the rear without removing it. The time complexity for this operation is O(1) .
- int size(): It returns the number of elements stored in the queue. The time complexity for this operation is O(1) .
- int isEmpty(): It indicates whether no elements are present in the queue or not. The time complexity for this operation is O(1) .
Difference between Linear and Non-linear Data Structures
Linear Data Structure: A linear data structure is one in which data items are ordered sequentially and each data member attached to its previous and next neighbouring elements.
Non Linear Data Structure: A Non-linear data structure is one in which data items are not ordered sequentially and each member can connect to other member through multiple paths.
Now let's understand the difference between both of them in detail.
| Linear Data Structure | Non Linear Data Structure |
|---|
| Data elements in linear data structure are ordered in sequential order, with each element connected to the previous and next element. | Data elements are connected hierarchically in a non-linear data structure. |
| They can be traversed completely in a single run. | They needed multiple runs to traverse them completely. |
| In this type of data structure, only a single level is involved. | In this type of data structure, multiple levels are involved. |
| In a linear data structure, memory is not utilized in an efficient way. | In a non-linear data structure, memory is utilized in an efficient way. |
| Examples: Arrays, Stack, Queue, Linked List. | Examples: Trees, Graphs, etc. |
Looking to excel in coding interviews? Our Java DSA course is your key to success. Enroll today and pave the way for a successful career.
Conclusion
- In linear data structure , data elements are ordered in a sequential order, with each element connected to the previous and next element.
- Arrays, Linked List, Stack, and Queue are the different types of linear data structures .
- Array elements store in a contiguous memory location but Linked list elements can be stored anywhere in the memory.
- Stack follows Last in First out and Queue follows First in First out.
- Both insert and delete operations inside stack and queue take O(1) time.
- In linear data structures memory is not efficiently utilized as compared to the non-linear data structures.







 stack data structure" width="864" height="200" />
stack data structure" width="864" height="200" />